Showing all 2 results
What is Suboxone?
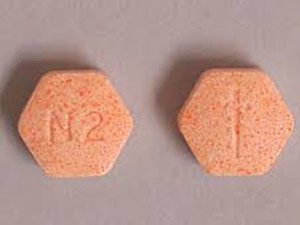
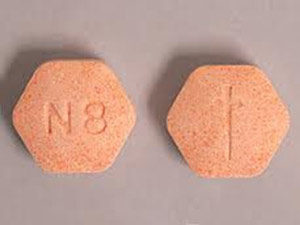
Suboxone is sublingual tablets containing buprenorphine and naloxone. It is available in the dosage strength of 2 and 8 milligrams of buprenorphine HCI with 0.5 and 2 milligrams of naloxone HCI. Suboxone tablets are uncoated hexagonal-shaped orange-colored pills having an imprint of “N2” and “N8” on one side.
Buprenorphine is a partial agonist at mu-receptor, while naloxone is an opioid receptor antagonist. Suboxone sublingual tablets also contain inactive ingredients povidone K30, mannitol, lactose, citric acid, corn starch, sodium citrate, acesulfame K sweetener, magnesium stearate, color additive FD & C Yellow No. 6, and a lime flavor.
Suboxone pills are preferable over Subutex as they have a comparatively low risk of dependence and abuse due to the presence of active ingredient naloxone.
Uses of Suboxone-
Buy Suboxone online for opioid dependence maintenance treatment. The tablets are helpful as a part of a complete treatment program, including psychosocial support and counseling.
Drug Addiction Treatment Act (DATA) states that prescription of suboxone for the treatment of opioid dependence should limit to healthcare providers or medical professionals who meet specific qualifying requirement, and who notified the Health and Human Services (HHS) Secretary of their intent for prescribing this medication for the treatment of opioid dependence and have a unique identification number assigned to them, that they must include on every prescription.
Side Effects of Suboxone –
Severe side effects of Suboxone tablets include:
- Central Nervous System and Respiratory depression
- Risk of addiction and abuse
- Opioid withdrawal
- Adrenal insufficiency
- Hepatic events or hepatitis
- Hypersensitivity reactions
- Elevation of cerebrospinal fluids
- Orthostatic hypotension
- Increased intracholedochal pressure
Some frequent Suboxone side effects include:
- Asthenia
- Chills or hot flushes
- Headache
- Abdomen pain
- Back pain
- Vasodilation
- Constipation
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Insomnia
- Sweating
- Rhinitis
- Flu syndrome
- Depression or anxiety
- Dizziness and drowsiness
Doses –
Follow the dosing instructions provided by a doctor after you buy Suboxone online. Progressively adjust the dosage of Suboxone sublingual tablets in increments or decrements of 2mg or 4mg to a level that suppresses withdrawal signs and symptoms of opioid.
The maintenance dose of Suboxone sublingual tablets is in the range of 4mg to 24mg per day, depending upon the response and needs of the individual patient.
For maintenance treatment by Suboxone sublingual tablets, there is no maximum duration of the therapy. Some patients may require years-long treatment.
Interactions –
Suboxone interacts with several drugs to produce undesirable effects. Some drug interactions of Suboxone may cause enhanced or decreased effectiveness of the medication. Clinically significant drug interactions of suboxone are:
- CNS depressants or benzodiazepines: central nervous system depressants such as alcohol or benzodiazepines interact with suboxone to cause additive pharmacologic effects such as respiratory depression, sedation, coma, or even death.
- Inhibitors of CYP3A4: Buprenorphine and CYP3A4, when mixed, increase the plasma concentration of buprenorphine that leads to increased opioid effects.
- CYP3A4 Inducers: Buprenorphine and CYP3A4 inducers, when mixed, decreases the plasma concentration of buprenorphine that leads to reduced efficacy and increased risk of withdrawal syndrome for patients who are physically or psychically dependent on the medication.
- Antiretrovirals: Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs) are metabolites of CYP3A4 inducer. The interaction of suboxone and NNRTIs does not show any significant pharmacodynamic effects, but it not advisable to take them together without proper medical supervision.
- Protease Inhibitors: Antiretroviral protease inhibitors elevates levels of buprenorphine and cause an excess of opioids in patients taking them together.
- Serotonergic drugs: The use of suboxone with medications that affect the serotonergic neurotransmitter system results in serotonin syndrome.
- Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs): MAOI interaction with suboxone causes serotonin syndrome or opioid toxicity such as respiratory depression or coma.
- Muscle relaxants: Suboxone increases neuromuscular blocking action of skeletal muscle relaxants and produces increased respiratory depression.
- Diuretics: Suboxone reduces the efficacy of diuretics by increasing the release of antidiuretic hormones.
- Anticholinergic drugs: The use of anticholinergic medications, along with suboxone, increases the risk of severe constipation or urinary retention, which leads to paralytic ileus.
Warnings & Precautions –
The special warnings and precautions associated with the use of suboxone are:
Risk of CNS and respiratory depression– Suboxone can cause fatal respiratory depression and death. Reports regarding coma and deaths after taking Suboxone show that concomitant use of central nervous system depressants or benzodiazepines and buprenorphine causes these effects.
Addiction, abuse, and misuse– Suboxone tablets contain buprenorphine, a Schedule III controlled substance. It has the same potential of abuse as other opioids. Follow all the precautions and prescriptions by a doctor to avoid the risk of dependence, addiction, and abuse.
Concomitant use with CNS depressants or benzodiazepines– Using Suboxone with benzodiazepines or other central nervous system depressants increases the risk of adverse reactions, overdose, and death. Avoid taking alcohol or any alcoholic beverages while on Suboxone medication.
Unintentional pediatric use– Suboxone may cause severe life-threatening respiratory depression in accidentally exposed children. Make sure to keep the medication away from the reach of children and properly destroy unused medicines.
Neonatal Opioid Withdrawal Syndrome– NOWS or neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome is the outcome of prolonged use of Suboxone during pregnancy. Suboxone can cause withdrawal symptoms in the newborn infant if taken by a pregnant woman.
Adrenal insufficiency– Use of opioids such as Suboxone can cause adrenal insufficiency, which includes non-specific signs and symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, dizziness, anorexia, weakness, fatigue, and low blood pressure.
Withdrawal on abrupt discontinuation– Suboxone causes severe symptoms of withdrawal if a person abruptly discontinues the medication.
Hypersensitivity reactions– hypersensitivity reactions such as hives, rashes, pruritus, and others are common by Suboxone. Do not give the medication to a person who is allergic to buprenorphine, naloxone, opioids, or any inactive ingredients of the medicine.
Alertness impairment– Suboxone causes impairment of alertness. It produces drowsiness, so it is not advisable to do any work that needs attention or alertness after taking Suboxone.
Risk of overdose– Suboxone has a risk of fatal overdose if not taken precisely as prescribed.